

Texas is one of the most popular states for people relocating in the U.S., and it’s easy to see why. With its booming economy, diverse landscapes, and lower cost of living compared to many coastal states, Texas offers a unique set of opportunities for new residents. Whether you’re moving from California, Florida, Louisiana, New York, or Colorado, there are some important things to know about making the Lone Star State your new home.
In this blog, we will provide tailored information for people moving from these five states to Texas, covering aspects such as lifestyle, housing, job opportunities, and local culture to help make your transition as smooth as possible. Additionally, we’ll include essential information related to driver’s licenses, car registration, and other driving-related processes to help you settle into your new life in Texas with ease.
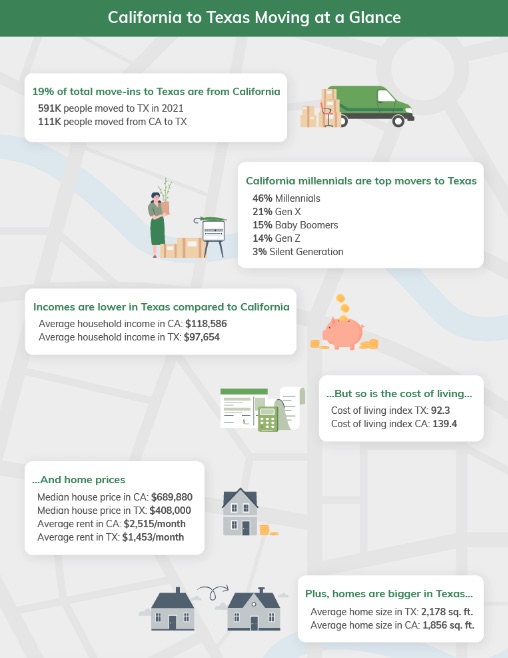
California residents have been flocking to Texas in droves, and for good reason. Texas offers a lower cost of living, no state income tax, and a growing job market, especially in tech and energy sectors.
What to Expect When Moving to Texas:
Top Cities to Consider: Austin, Dallas, Houston, and San Antonio.
Things to Know:
Floridians who make the move to Texas often find it to be a refreshing change, especially considering the lower cost of living and job growth in sectors like technology and healthcare.
What to Expect When Moving to Texas:
Top Cities to Consider: Austin, Dallas, Houston, and San Antonio.
Things to Know:
Louisiana residents looking to relocate to Texas can expect to find similar cultural influences, such as a strong culinary scene and a love for sports, but with the added benefits of better job opportunities and a more favorable tax environment.
What to Expect When Moving to Texas:
Top Cities to Consider: Houston, Dallas, Austin, and San Antonio.
Things to Know:
New Yorkers looking to escape the high cost of living and harsh winters will find Texas a welcome change. The state’s economic opportunities, growing tech scene, and more affordable housing are a few reasons why Texas is becoming a top destination for those leaving the Empire State.
What to Expect When Moving to Texas:
Top Cities to Consider: Austin, Dallas, Houston, and San Antonio.
Things to Know:
For Coloradans used to the great outdoors and stunning mountain views, moving to Texas offers an entirely different set of experiences. From the vast plains of West Texas to the bustling cities like Austin, Texas provides a new adventure for those seeking a change.
What to Expect When Moving to Texas:
Top Cities to Consider: Austin, Dallas, Houston, and San Antonio.
Things to Know:
Moving from California to Texas involves more than just a change of scenery—it means adapting to different state laws. From income taxes to driver’s license regulations to family laws, understanding the key differences will help ensure a smooth transition. Don’t forget to update your Texas driver’s license and car registration as soon as possible to comply with local laws. By staying informed, you’ll be able to fully enjoy your new life in the Lone Star State.